Nombre:
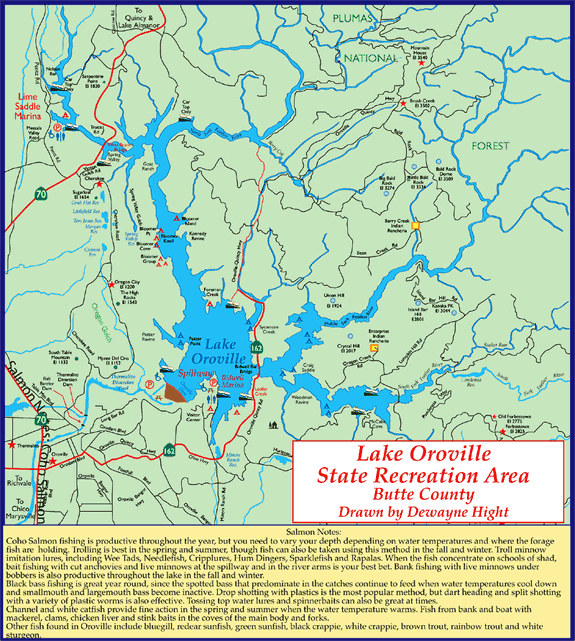
Presa de Oroville
Otro:
Localización:
View Larger Map
Récord: 4360 hm³
Récord de Altura: 235 m
Tipo: Presas
Categoría: Tierra Roca
Foto:

Voto:
Continente: América
País: Estados Unidos
Localización: Oroville, California
Año: 1961-1968
Estado: Terminado
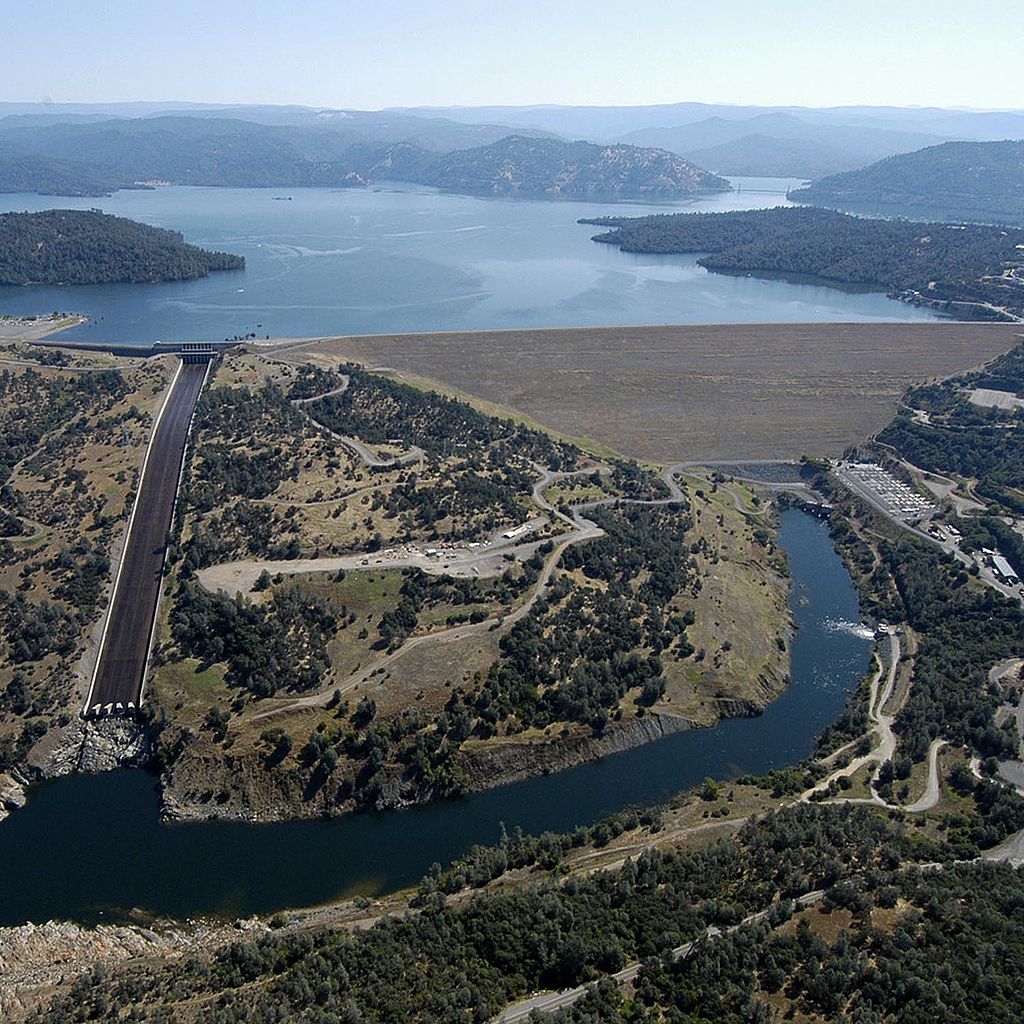
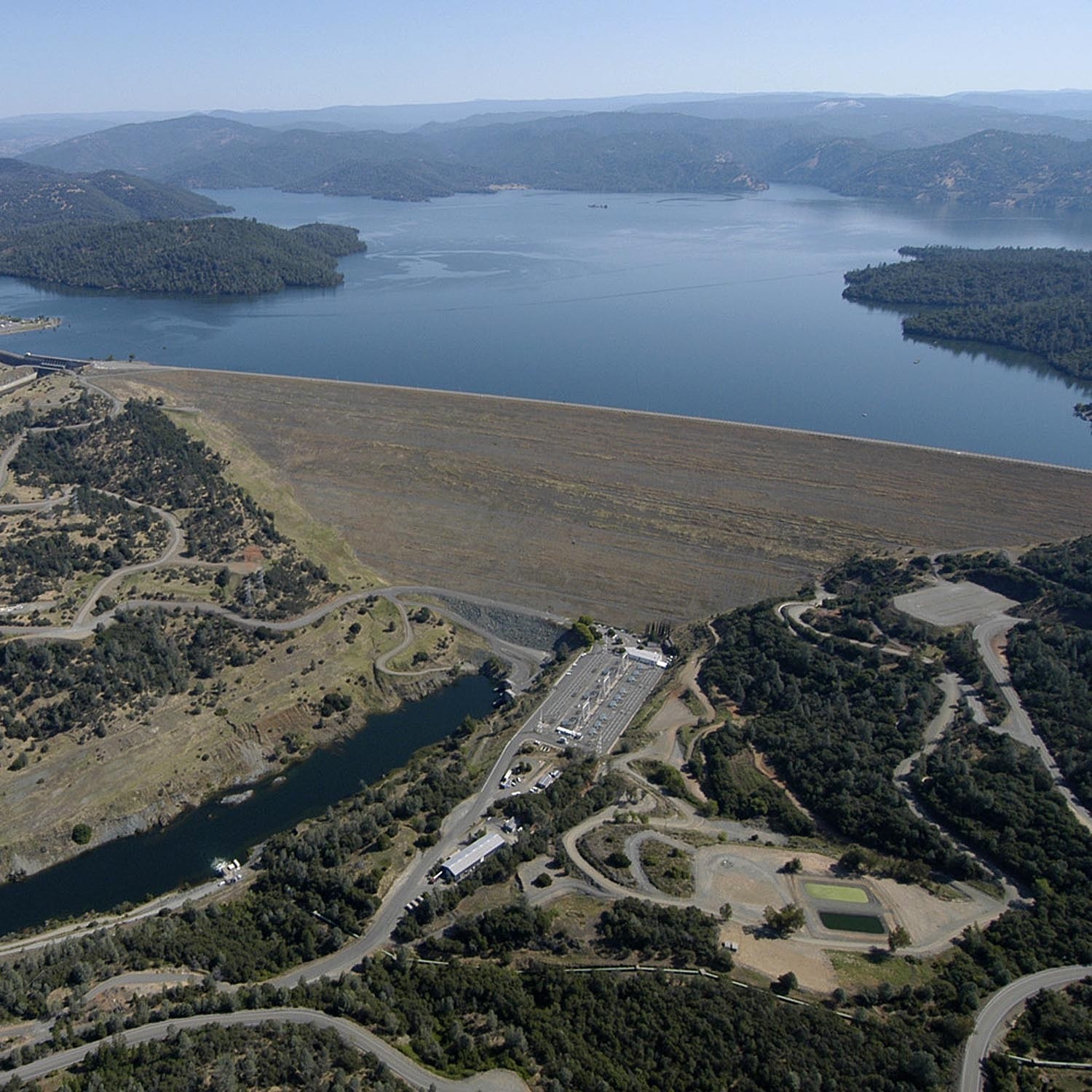
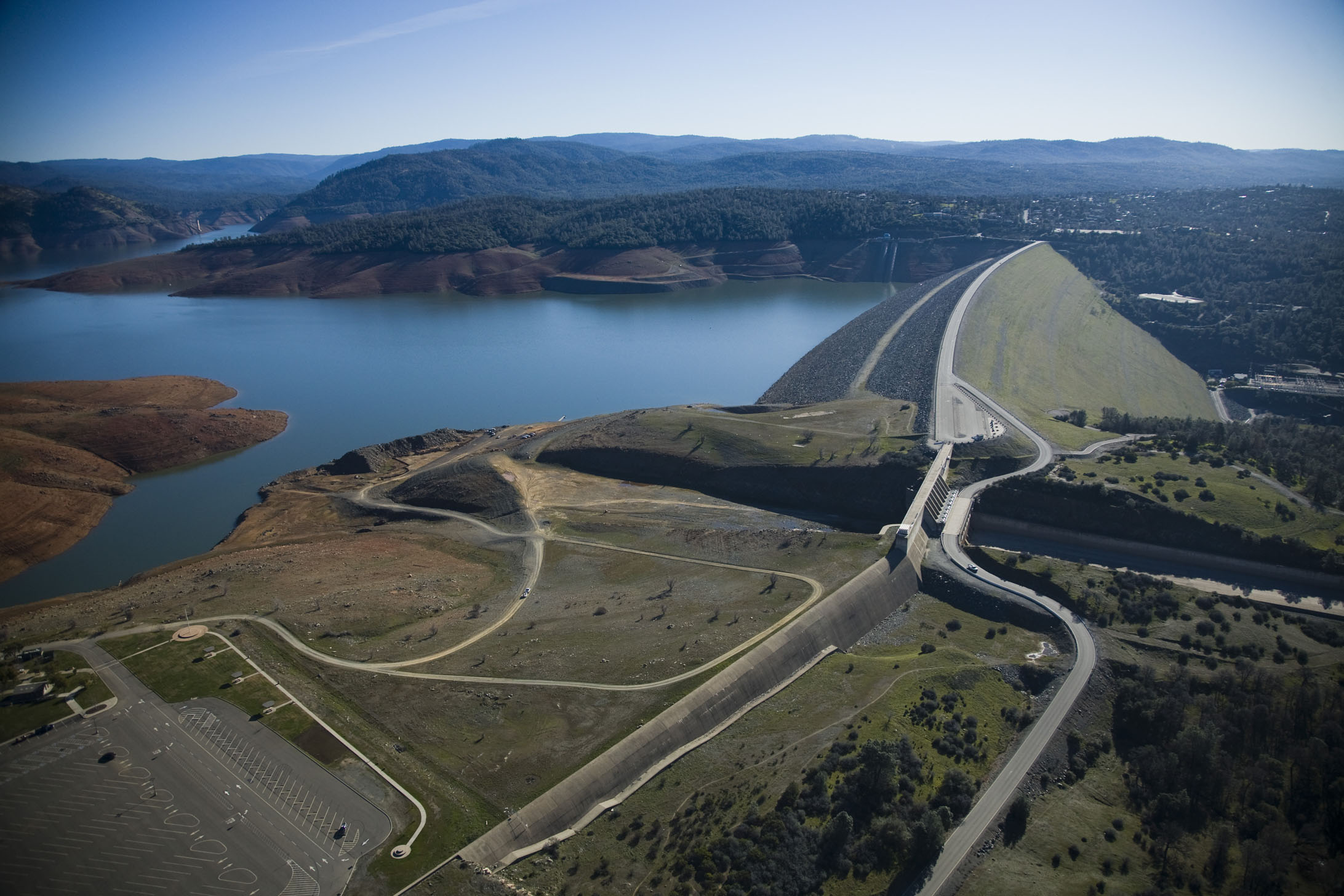
Descripción:La presa de Oroville es una presa sobre el río Feather por encima de la ciudad de Oroville en el condado de Butte, California, Estados Unidos. Crea el lago Oroville, genera electricidad y proporciona agua para beber y la irrigación del Valle Central de California y el Sur de California. La presa, el lago, y otras instalaciones son propiedad del estado de California Department of Water Resources quien lo administra y forma parte del Proyecto Hídrico del estado de California (SWP).



http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Presa_de_Oroville
Lake Oroville was born Nov. 14, 1967, when the second of two diversion tunnels that had carried the Feather River beneath the embankment during construction was blocked.
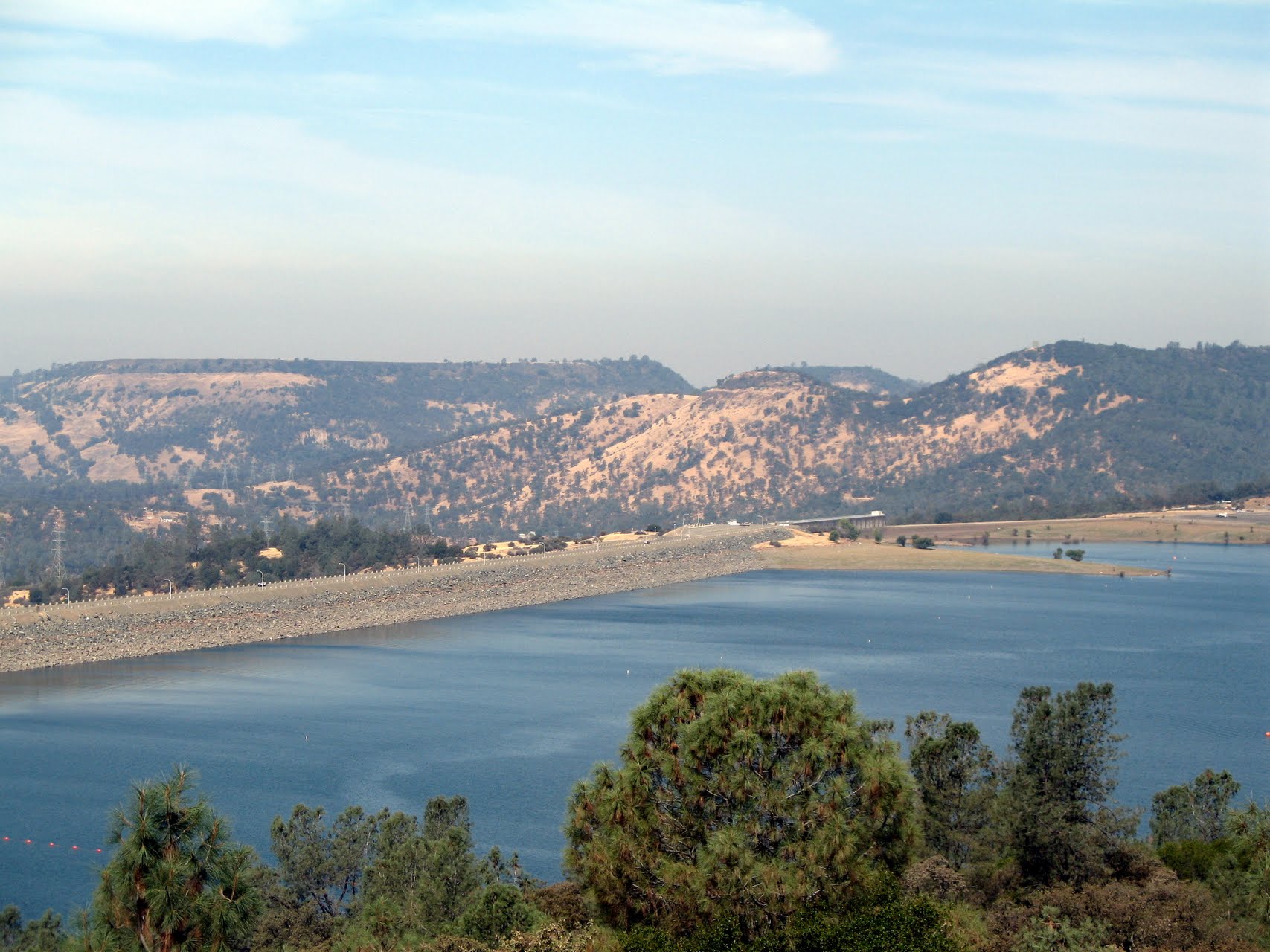
Oroville Dam is the tallest and one of the largest earthen dams in the United States. The dam, completed in 1968, stands 770 feet high with a crest (top of the dam) 6,920 feet long. Over 80 million cubic yards of material were needed to build the Oroville Dam. There is enough material to build a two-lane highway around the earth in the Dam.
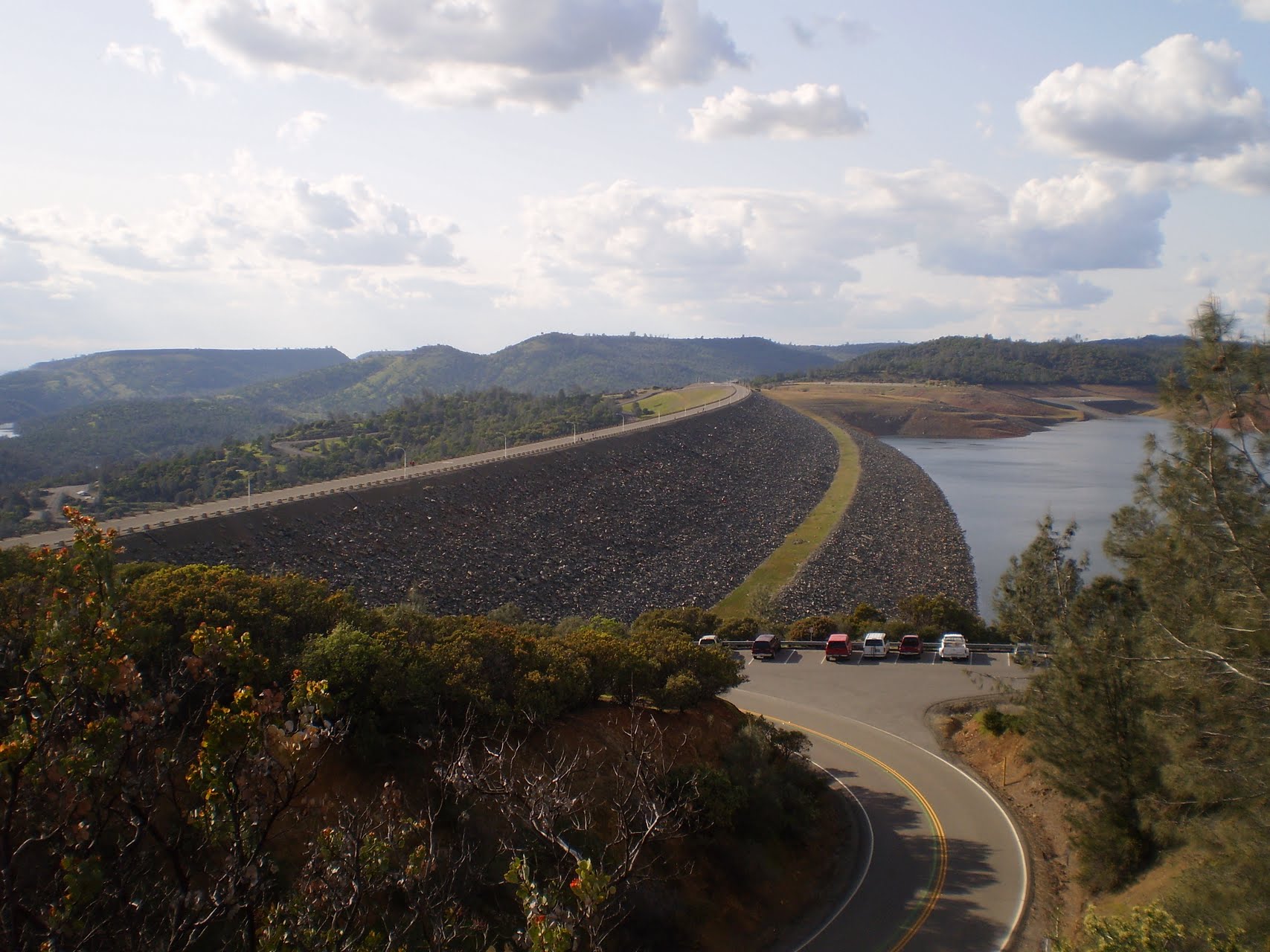
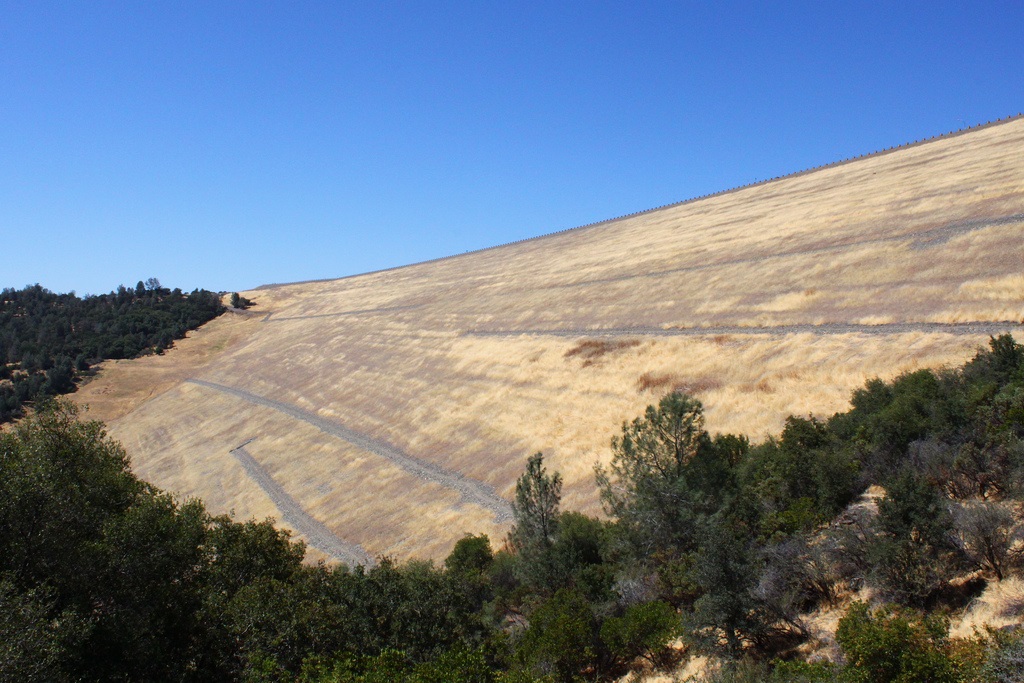
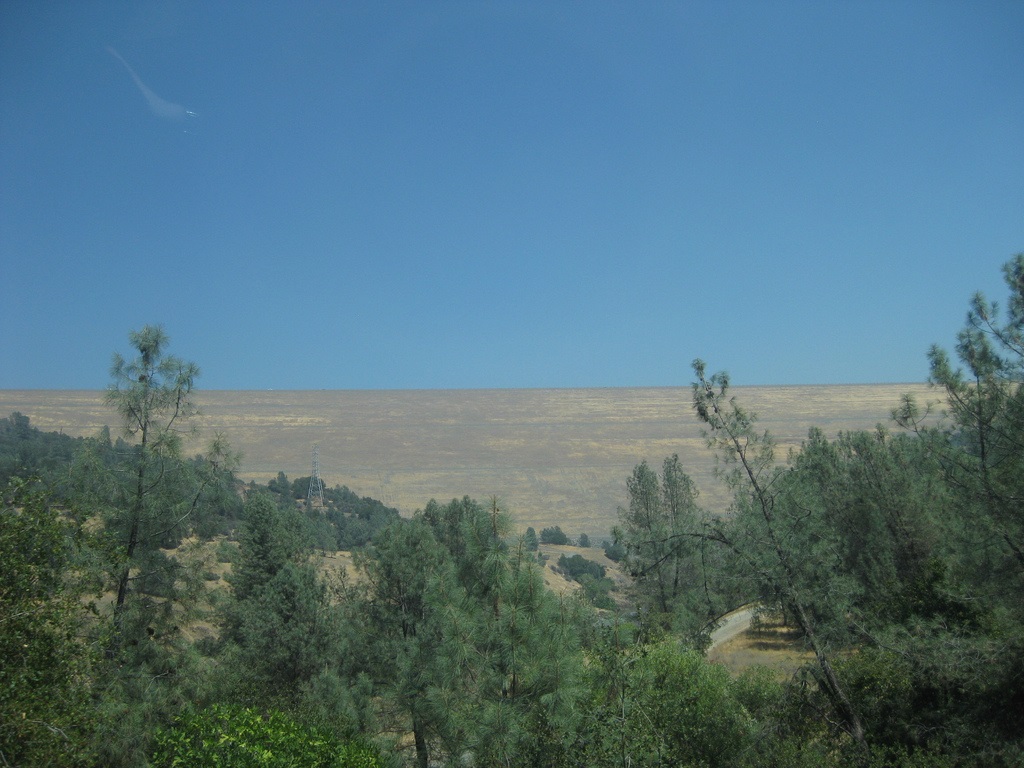



The dam's inner core is a thin layer made of clay material which resists seepage. Gold dredged tailings (sand & gravel left from the early 20th century gold dredging along the Feather River) make up the remainder of Oroville Dam.
Beneath the dam a giant cavern almost as large as the State Capitol Building has been hollowed out to house six power generation units. Coupled with four additional units in the Thermalito Power plant, they will generate more than 2.8 billion kilowatt-hours of power annually.
Other facilities in the State Water Project are the Thermalito Forebay and Afterbay, holding reservoirs located downstream that enable utilization of a "pump-back" procedure whereby water released from Lake Oroville to generate power during "peak need" periods, will be pumped back into the lake during off-peak periods for recalculation through the powerplants.
Surface Area (maximum) 24 sq. miles
Capacity 31/2 million acre-feet
Shoreline (maximum) 167 miles
Depth (maximum) 690 feet
Length (maximum) 21 miles
http://www.oroville-city.com/sightseeing/thedam.html
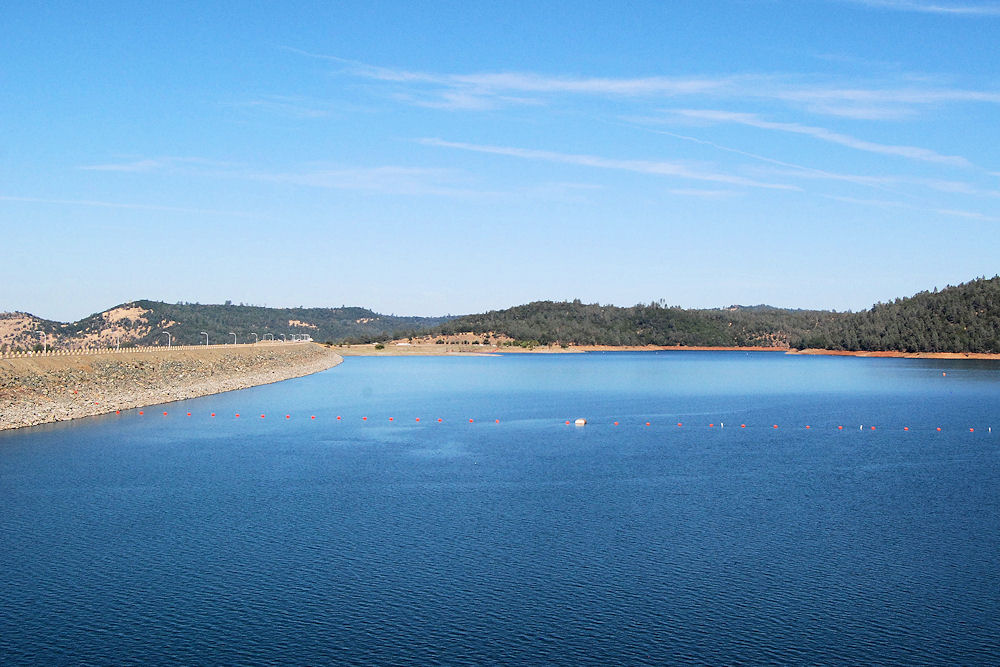
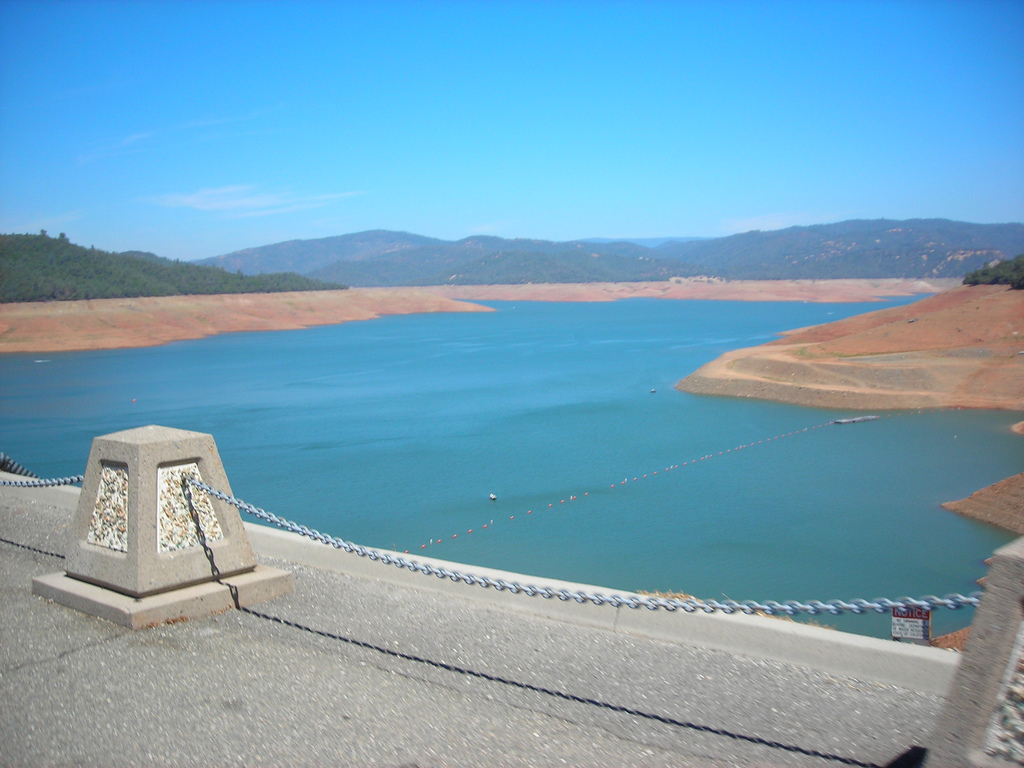
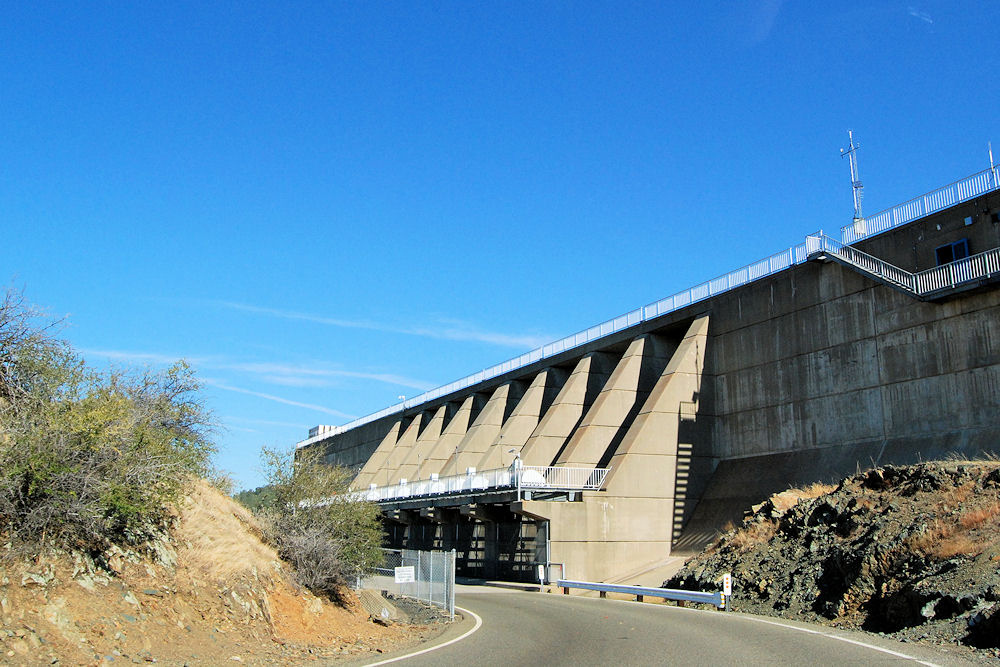



Oroville Dam is an earthfill embankment dam on the Feather River east of the city of Oroville, California in the United States. At 770 feet (230 m) high, it is the tallest dam in the U.S.[6] and serves mainly for water supply, hydroelectricity generation and flood control. The dam impounds Lake Oroville, the second largest man-made lake in the state of California, capable of storing more than 3.5 million acre-feet (4.4 km3),[7] and is located in the Sierra Nevada foothills east of the Sacramento Valley.
Built by the California Department of Water Resources (DWR), Oroville Dam is one of the key features of the California State Water Project (SWP), one of two major projects passed that set up California's statewide water system. Construction was initiated in 1961, and despite numerous difficulties encountered during its construction including multiple floods as well as a major train wreck on the railroad line that was utilized for the transportation of materials to the dam site, the top main causeway reached completion in 1967 and the entire project was ready for use in 1968. The dam began to generate electricity after completion of the Edward Hyatt Pump-Generating Plant, then the country's largest underground power station.
Since its completion in 1968, the Oroville Dam has allocated the flow of the Feather River from the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta into the State Water Project's California Aqueduct, which provides a major supply of water used for irrigation in the San Joaquin Valley as well as municipal and industrial water supplies to coastal Southern California, and has prevented large amounts of flood damage to the area – more than $1.3 billion between the years of 1987 and 1990.[8] The dam has confined fish migration up the Feather River and the controlled flow of the river as a result of the Oroville Dam has affected riparian habitat. Multiple aims at trying to counter the dam's impacts on anadromous fish have included the construction of a salmon/steelhead incubator on the river which began shortly after the dam was completed.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oroville_Dam
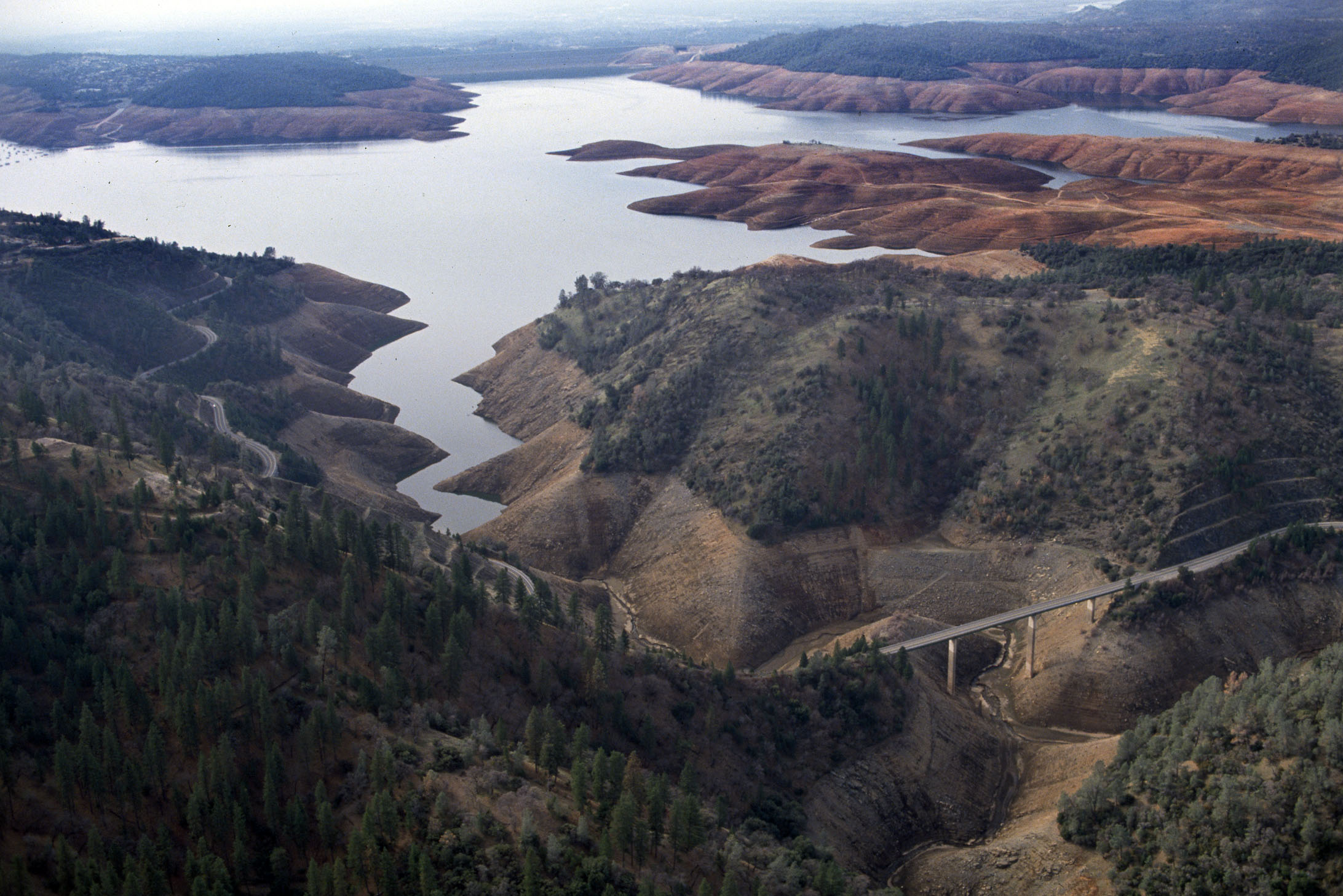
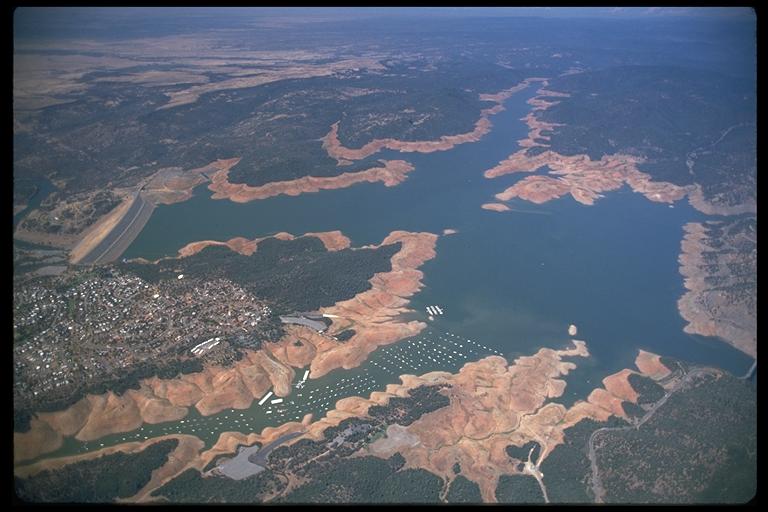
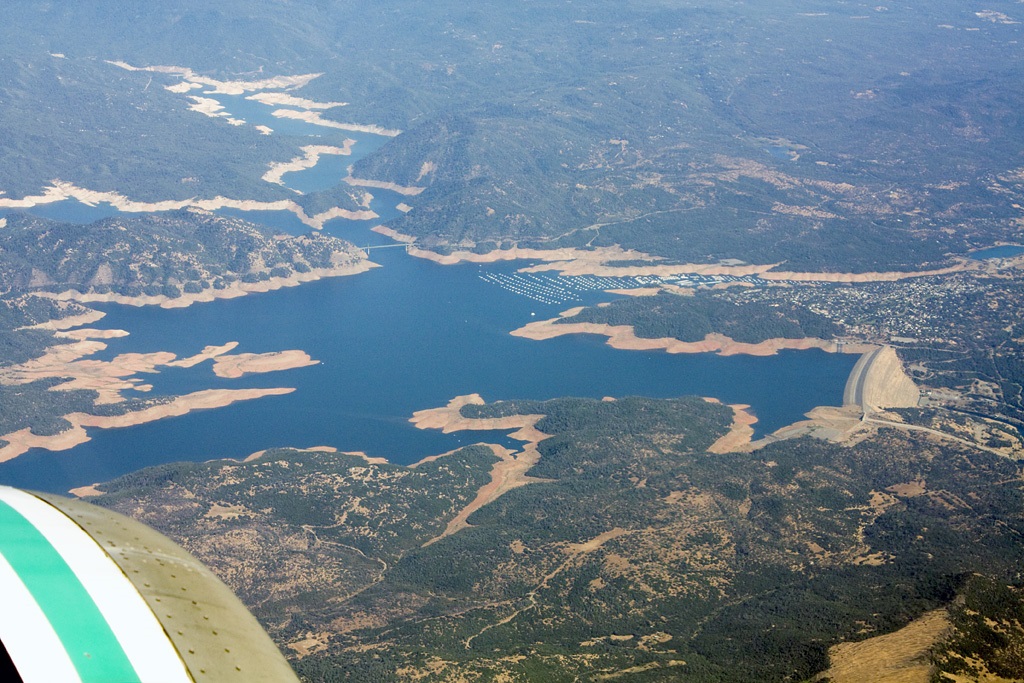



Oroville Dam
Oroville Dam is an earthfill embankment dam on the Feather River east of the city of Oroville, California in the United States. At 770 feet (230 m) high, it is the tallest dam in the U.S.[6] and serves mainly for water supply, hydroelectricity generation and flood control. The dam impounds Lake Oroville, the second largest man-made lake in the state of California, capable of storing more than 3.5 million acre-feet (4.4 km3),[7] and is located in the Sierra Nevada foothills east of the Sacramento Valley.
Built by the California Department of Water Resources (DWR), Oroville Dam is one of the key features of the California State Water Project (SWP), one of two major projects passed that set up California's statewide water system. Construction was initiated in 1961, and despite numerous difficulties encountered during its construction including multiple floods as well as a major train wreck on the railroad line that was utilized for the transportation of materials to the dam site, the top main causeway reached completion in 1967 and the entire project was ready for use in 1968. The dam began to generate electricity after completion of the Edward Hyatt Pump-Generating Plant, then the country's largest underground power station.
Since its completion in 1968, the Oroville Dam has allocated the flow of the Feather River from the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta into the State Water Project's California Aqueduct, which provides a major supply of water used for irrigation in the San Joaquin Valley as well as municipal and industrial water supplies to coastal Southern California, and has prevented large amounts of flood damage to the area – more than $1.3 billion between the years of 1987 and 1990.[8] The dam has confined fish migration up the Feather River and the controlled flow of the river as a result of the Oroville Dam has affected riparian habitat. Multiple aims at trying to counter the dam's impacts on anadromous fish have included the construction of a salmon/steelhead incubator on the river which began shortly after the dam was completed.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oroville_Dam
http://djkuba.tripod.com/index-5.html
http://www.rbbassfishing.net/2012/01/29/us-anglers-choice-pro-am-to-hit-lake-oroville-in-february/
Vídeo:
Contador: 10541
Inserción: 2013-06-21 13:13:08
Lugares a visitar en un radio de 100 km (en línea recta)
Mapa de los lugares a 100 km (en línea recta)
Mostrando Registros desde el 1 hasta el 0 de un total de 0
Visitas |
Más visitados Basílica de San Marcos 149070 Catedral de Notre Dame (París) 137693 Torre de Pisa 128207 Monte Saint-Michel 97328 Presa de las Tres Gargantas 73665 |
Incorporaciones |
Comentarios Arq. Jaime Fuentes Flores Torres Obispado EXTRAORDINARIO . FELICIDADES . Un Cordial saludo Directivos y Personal de ... hazola Cúpula de la Roca gracias me... gera Buenos Aires las mejores fotos de la mejor ciudad del... Daniel M. - BRASIL San Francisco ... PEQUE Presa Chicoasén SERA QUE ALGUIEN ME PUEDE DAR MAS INFORMACIÓN DE ESTE PROYECTO ESTUDIO EN LA UNACH Y ES PARA UN... |
 Tweet
Tweet